
Spring MVC Primer Part 1
Recently, I had to dive into Spring Framework for a project at work. I choose Amuthan G's Spring MVC Beginner's Guide to get up to speed quickly. What follows are my brain-dump from what I learned reading the book.
Spring MVC leverages the MVC ( Model-View-Controller) architecture to provide a framework for building web applications in java. This framework makes it easy to modularize the code for views, data and business logic while providing the high level efficiency of Java. The basic division of work is as follows:
• The Model part encapsulates the application data and generally consists of Plain Old Java Objects (POJO).
• The View part deals with the rendering of the html to the users. Views can be dynamically generated with dynamic blocks using JSP and JSTL.
• The Controller part handles the requests, maps them to corresponding services, fetches the required data from models and feeds them to the views for rendering to the clients.
The Spring MVC framework is configured around a dispatcher servlet. This dispatcher servlet is responsible for mapping requests, calling the required controllers, getting the logical view name and finally returning the view after resolving the view name. A typical workflow is as follows:
- Dispatcher servlet gets an HTTP request.
- Dispatcher servlet consults the request mapper to call the appropriate controller.
- The controller calls the appropriate service depending on the request method, sets model data and returns a view name.
- Dispatcher servlet consults the view resolver to find the appropriate view that corresponds to the view name returned by controller.
- Finally, dispatcher servlet feeds the model data to the view and returns the view as an HTTP response. The necessary configurations for dispatcher servlet, handler mapping and view resolver is generally implemented using xml files but can also be done using annotations.
Detailed Discussion
Web.xml
The servlet mapping is described in the web.xml file. The dispatcher servlet works as the front controller for the application. So, we define this servlet in the web.xml file and map urls to it.
DispatcherServlet-servlet.xml
This is the application context. It is a container of objects. Objects and their associations are stored inside the container when the project is deployed. These objects are knows as beans. Properties of these beans are configured in this file like mvc-annotation, viewResolvers, etc. Context component scan is used to search in the controller files for url mappings. Controller methods map urls and return logical views. Dispatcher resolves the logical views and returns the real view.
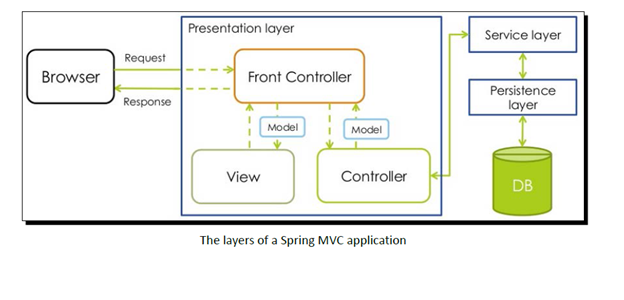
Application Architecture
Generally, spring projects are developed in an n-tier architecture. There are 4 tiers or layers in an enterprise level spring mvc application:
- Presentation
- Service
- Persistence (Repository)
- Domain (Model)
Presentation Layer
Dispatcher, views, controllers – all are part of the presentation layer.
Service Layer
This layer is used for all the business logic. We use interfaces here for loose coupling between layers. Service layer communicates with the persistence layer for accessing data and maintains transactional behaviour.
Persistence Layer
This layer is used to read and write data from and to the database. Interfaces are used in this layer to keep the Service layer and the Persistence layer decoupled. Repository objects implement the interfaces. We use the interface in the services to get the data. The @autowired notation asks the application context to refer to appropriate implementation of the interface. As with @controller, the application context also scans and create beans for @Repository and @service annotations as well.
Domain Layer:
This layer typically consists the model representation of the database entities.
So, in summary, presentation layer deals with request handling and mapping. Controllers from Presentation layer call interfaces from Service layer. Service layer relies on the Persistence layer for the CRUD operations. Service layer ensures transactional behaviour and @transactional annotation is used in Service layer. Persistence layer accesses the data storage through Repository classes and uses the Domain representations to interchange data between application and database. Below is a diagram that depicts the layered interaction in Spring MVC.
Read the next part here
